For the first time, an unmanned surface vehicle (USV) recently completed a seabed cable route survey that included various water depths and strong currents, all while facing difficult wind and sea conditions in the Bering Sea offshore Alaska.
For the first time, an unmanned surface vehicle (USV) recently completed a seabed cable route survey that included various water depths and strong currents, all while facing difficult wind and sea conditions in the Bering Sea offshore Alaska.
ASV Global and TerraSond worked together to complete this survey, according to a news release.
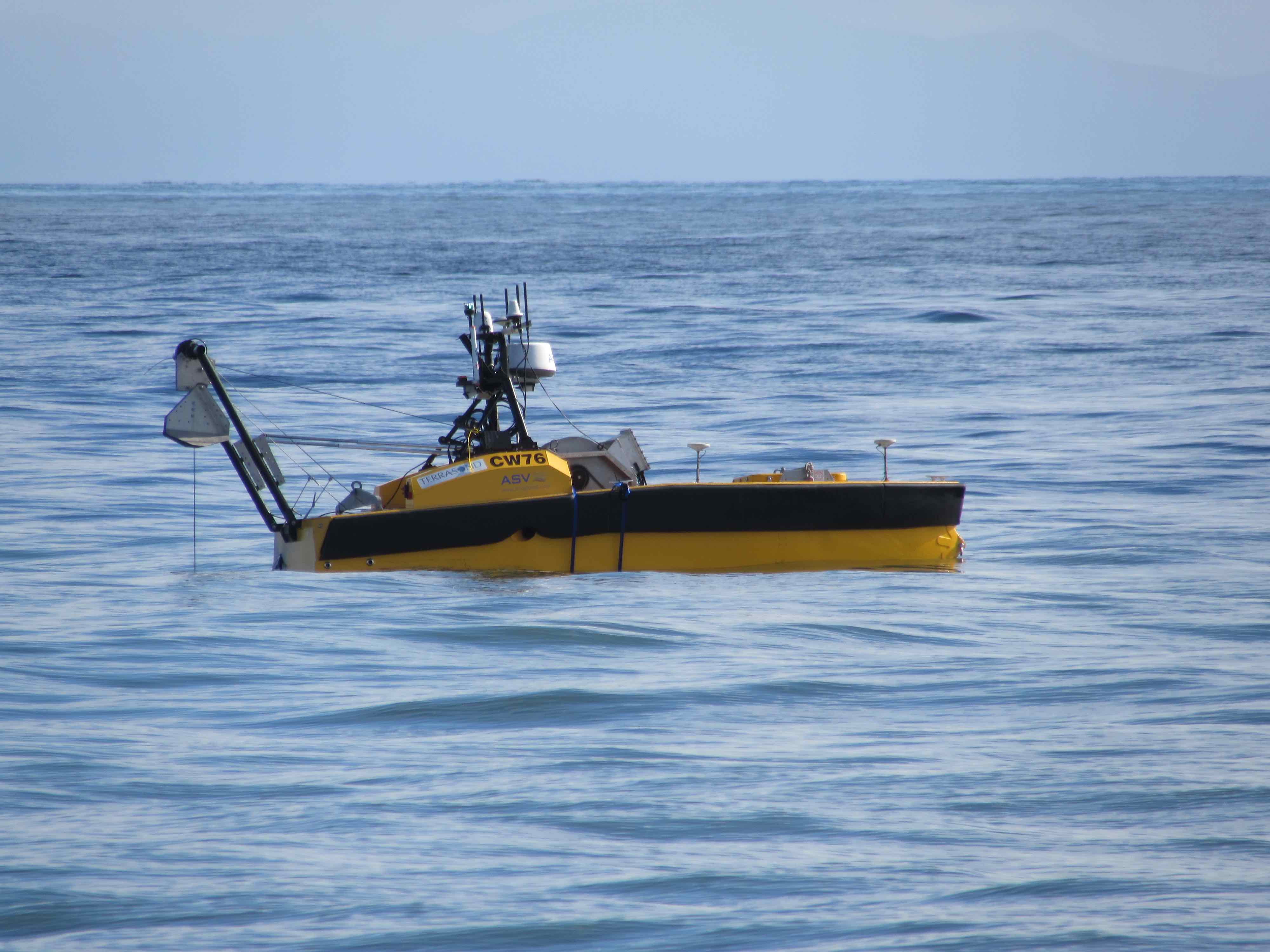
The project was mobilized immediately following a 9,000km nautical charting survey by Terrasond, of which 4,750km (53 percent) was executed by an ASV Global C-Worker 5 autonomous surface vehicle (ASV). The cable route survey required a new payload that included a hull mounted multibeam sonar, a sub-bottom profiler, and a towed sidescan sonar with 250m of armored sonar cable.
The payload swap on the ASV was integrated, calibrated, and demonstrated in the field in less than 48 hours. The C-Worker 5 system successfully executed 1,220 km of cable route survey lines.
The C-Worker 5 was remotely monitored using ASV Global’s ASView control system from a station on TerraSond’s mother ship. ASView used exported .dxf survey lines from the TerraSond survey planning system to autonomously execute the survey with minimal human intervention.
“This is a landmark achievement for ASV technology, and we are pleased to be supporting TerraSond in this effort,” said Thomas Chance, CEO of ASV Global, according to the release. “The fast re-tasking of the system from one type of mission to another illustrates the flexibility of the C-Worker ASV, and its consistent performance in difficult sea conditions further underscores the value of this highly efficient approach to offshore operations.”
The C-Worker 5 is designed for up to five days of endurance at survey speeds of up to 7 knots, minimizing launch and recovery options and increased survey efficiency.