The European GNSS Agency has published an online White Paper on European Global Navigation Satellite Systems, asserting that use of Galileo and its corrections via the European Navigation Overlay Service (EGNOS) are essential for the safe and reliable navigation of drones.

Whitepaper by the European GNSS Agency
The report further states that GNSS receivers are implemented on almost all new commercial drones as standard.
Market statistics cited in the report predict that European drone service revenues will nearly double from EUR 32 million in 2018 to approximately EUR 60 million by 2020, eventually rising to EUR 150 million by 2023.
With increasing demand for beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS) operations, GNSS with augmentations is the most obvious choice of technology for navigation — although not the only one, according to the authors. Galileo-enabled receivers are borne by more than 30% of the receivers used for drone applications, while many also implement EGNOS corrections to increase accuracy.
The paper provides a market perspective of GNSS for drones, together with a summary of applications powered by EGNSS and the results of testing campaigns that show the benefits of EGNSS vs GPS in different operational contexts. With Galileo satellites in addition to GPS, drones can use signals from more satellites for position determination, improving both the accuracy and availability of received signals.
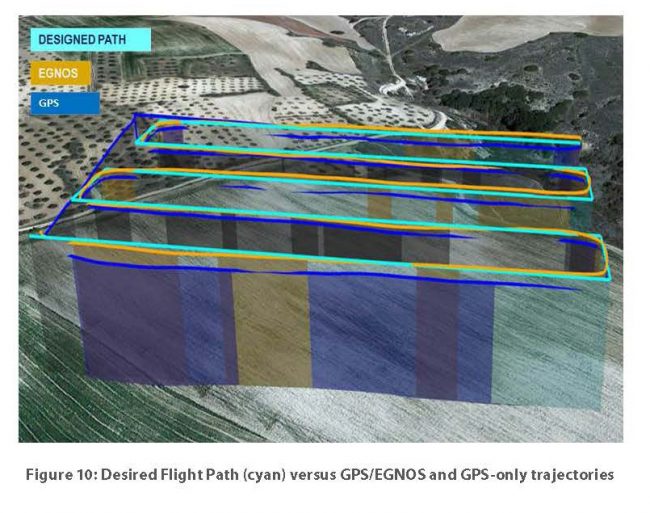
Flight path differences with GPS only and GPS with EGNOS corrections. Image: GSA
Galileo also offers distinct and unique features that benefit drone operations, according to the report. For example, Galileo’s authentication will provide additional trust in the position, which is more robust against intentional or unintentional interferences. EGNOS corrections also provide improved robustness over Europe and higher safety of navigation as well as improved accuracy, which is especially relevant in the vertical axis for drone operations.
The paper targets drone manufacturers and operators, but also entrepreneurs planning to offer new services with unmanned platforms.
Table of Contents:
Introduction
Background
- Drone Market
- Regulatory Status
- EASA
- JARUS
- EUROCONTROL
- EUROCAE
- European initiatives – SESAR 11
Localisation of drones
- Current technologies used for drone positioning and navigation
- Stand-alone GNSS
- Augmented GNSS
EGNSS benefits for drones
- EGNOS accuracy and integrity
- Flight demonstrations with EGNOS-enabled receivers
- Galileo accuracy and availability in the multi-constellation concept
- Flight demonstrations with GPS/GPS + Galileo
- Simulations of RTK GPS/GPS + Galileo positioning
- Galileo High Accuracy Service (HAS)
Galileo authentication features
GSA-supported projects: Demonstrators and application development for E-GNSS in drones
- Equipment Development and Integration
- Operations
- Applications development
- Agriculture
- Energy
- Mapping/Surveying
- Public Safety
Conclusions
List of acronyms